Expanded Core Curriculum vs. General Education: A Teacher's Guide for Teaching Visually Impaired Students
Sep 16, 2025
You’ve just welcomed a new student into your classroom. They're bright and eager to learn, and now you learn that they have a
Someone mentions the
Understanding the General Education Core Curriculum
First, let's start with what we all know: the
English Language Arts Mathematics Science Social Studies and History
The Critical Need for Something More
Introducing the Solution: What is the Expanded Core Curriculum (ECC)?
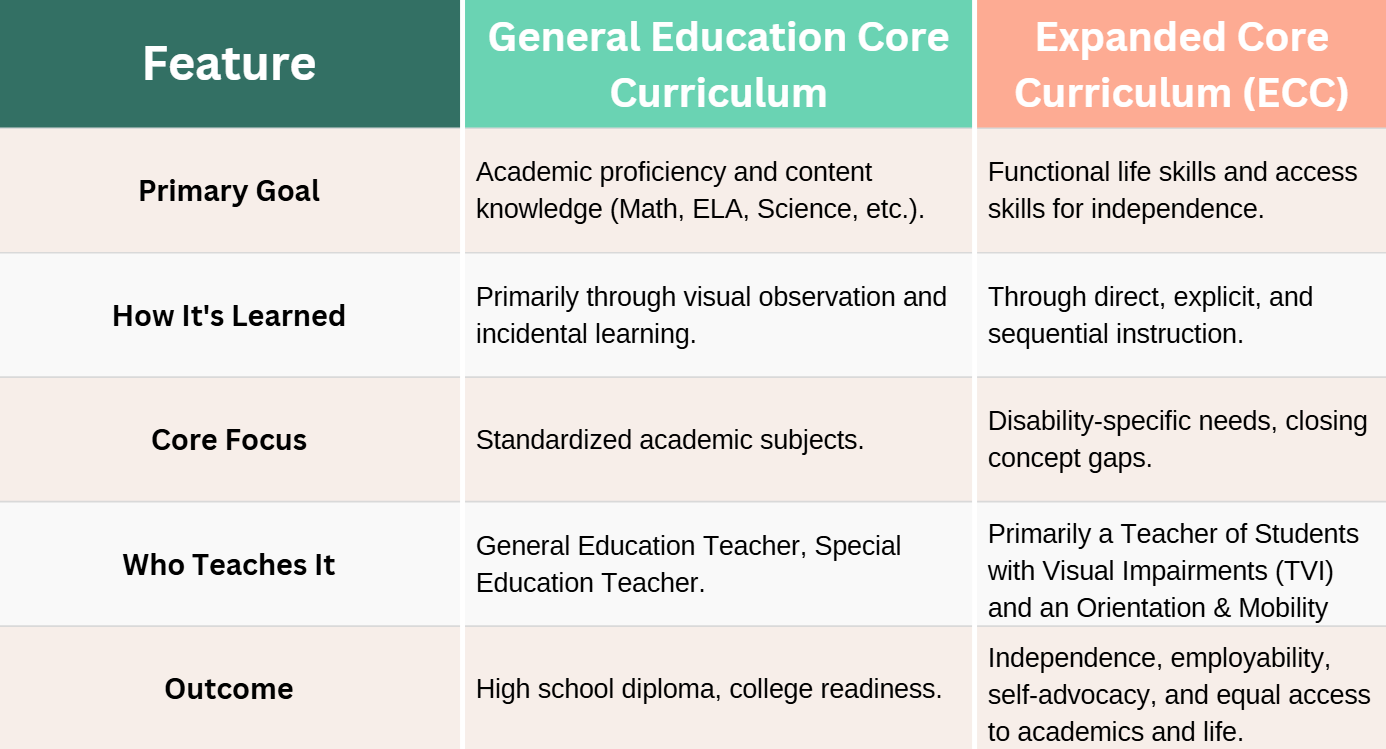
The Key Distinction: General Education Core Curriculum vs. Expanded Core Curriculum
A Deep Dive: The 9 Areas of the Expanded Core Curriculum
Compensatory or Functional Academic Skills: This is where we bridge the gap to the general curriculum. It includes communication modes like Braille, using a screen reader, accessing large print, and learning to use an abacus for math.Orientation and Mobility (O&M): Taught by a certified O&M Specialist, this is the skill of knowing where you are in space and moving safely and efficiently through your environment. It includes everything from using a long white cane to navigating a school hallway or a city block.Social Interaction Skills: So much of social communication is visual—body language, facial expressions, eye contact. Students with VI need direct instruction on how to interpret social cues, initiate conversations, and present themselves confidently.Independent Living Skills (Daily Living Skills): This area covers the skills needed to manage daily life: cooking, cleaning, personal grooming, managing money, and organizing belongings. It’s about building the confidence forindependent living .Recreation and Leisure Skills: This involves adapting hobbies and sports for a person with a visual impairment and introducing them to new ones (like goalball or tandem biking) to promote physical and social well-being.Career Education: This is a broad area that includes exploring career options, understanding one's strengths and interests, learning job-seeking skills, and understanding workplace etiquette.Assistive Technology (AT): This is one of the most vital areas. It covers the full range of technology, from low-tech devices like magnifiers to high-tech tools like screen-reading software (e.g., JAWS, VoiceOver), refreshable braille displays, and CCTV magnifiers.Sensory Efficiency Skills: This involves teaching a student how to use all their remaining senses, hearing, touch, taste, smell, to gather information from the environment. For example, learning to listen to traffic patterns to cross a street or using tactile skills to identify objects.Self-Determination: This is the skill of being your own advocate. It involves understanding your visual impairment, knowing what accommodations you need, and being able to confidently explain those needs to teachers, employers, and peers.
The ECC in the General Education Classroom
Push-In Services: This is when the TVI or O&M specialist comes into your classroom. They might co-teach a lesson, discreetly support the student during an activity, or model a strategy that you can use later. For example, during a science lab, the TVI might work alongside the student, providing tactile models and verbal descriptions to ensure they can participate fully. This is a powerful way for you to see accessibility strategies in action.Pull-Out Services: This is when a student is pulled from the classroom for intensive, one-on-one instruction in a specific ECC skill. For example, a student might leave class for 30 minutes to work on Braille with their TVI or to learn a new cane route with their O&M specialist. A good vision team will always strive to schedule pull-out services during less critical academic times, but even when a student misses part of a core class, the skills they are learning are designed to feed directly back into their ability to access your curriculum.
Your Role as an Empowered Partner
Related Articles:
- Making the Expanded Core Curriculum Work: A Practical Guide for Every Educator
- 3 BIGGEST Mistakes Teachers Make with Blind Students (and What to Do Instead)
- The 3 Key Strategies to Increasing Your Learners' Independence without Burning Out
- The Impact Of Visual Impairment On Learning
topics covered: Expanded Core Curriculum, visual impairment, general education, visually impaired students, ECC for VI, special education, assistive technology, orientation and mobility, daily living skills, compensatory skills, vision impairment education, inclusive classroom, braille instruction, TVI services, low vision students, concept gaps vision, push-in services, pull-out services, FAPE, IEP goals.

